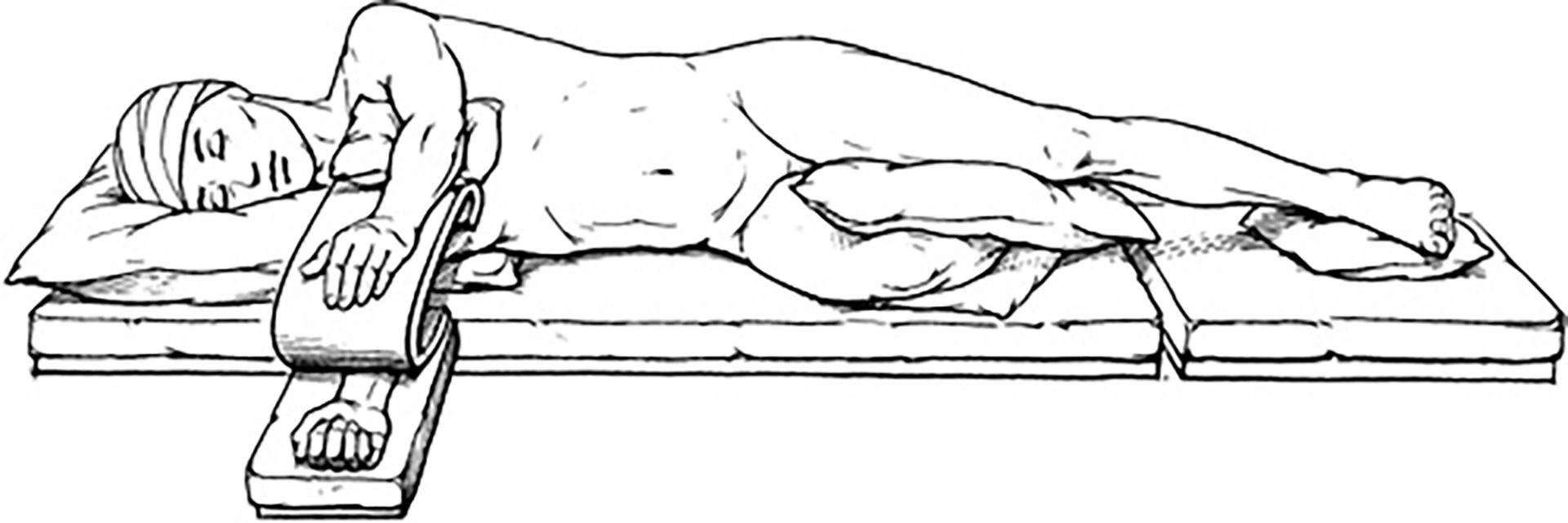
Lateral Decubitus Positioning
Lateral Decubitus
This position is most often used for procedures requiring access to the thorax, retroperitoneal structures, hip or shoulder. Flexion of dependent leg and hip helps keep alignment and stabilizes pt.
Padding between legs and on lateral aspect of dependent leg protects peroneal nerve.
Padding between legs and on lateral aspect of dependent leg protects peroneal nerve.
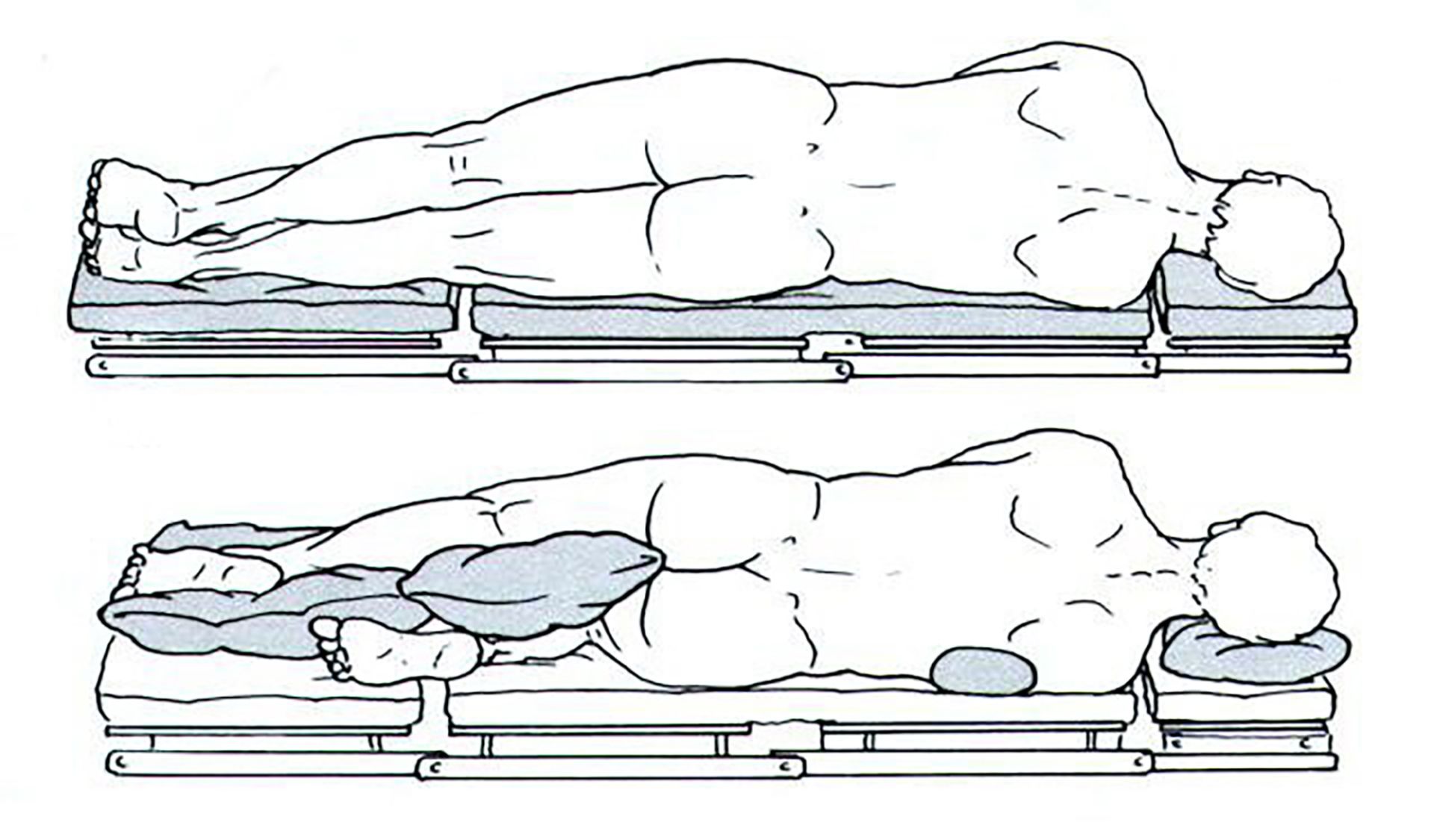
Ensure alignment of head with spine to prevent any occlusion of carotid/vertebral arteries, compromise of perfusion to head, impairment of jugular venous drainage and thus increased intracranial pressure (if drainage blocked).
Proper arm support. Upper arm elevated to prevent compression/stretch of brachial plexus. Monitor pulse and capillary refill in dependent and nondependent arm to ensure sufficient circulation.
Proper arm support. Upper arm elevated to prevent compression/stretch of brachial plexus. Monitor pulse and capillary refill in dependent and nondependent arm to ensure sufficient circulation.